D-ILA Device Technology
Technical Overview
The proprietary D-ILA*¹ device is used in 4K and 8K imaging markets.
It achieves high-brightness, high-resolution image reproduction.
*¹ D-ILA stands for Direct-drive Image Light Amplifier.
The D-ILA device is a high-definition reflective liquid-crystal panel uniquely developed by JVCKENWOOD.
It combines high brightness and high resolution by reflecting light that has passed through the liquid-crystal layer using pixel electrodes with a high aperture ratio of over 90%.
In addition to projectors equipped with D-ILA devices for the expanding 4K (4096 × 2160 pixels) and 8K (8192 × 4320 pixels) imaging markets, we are also applying this technology to non-visual fields such as optical communications.
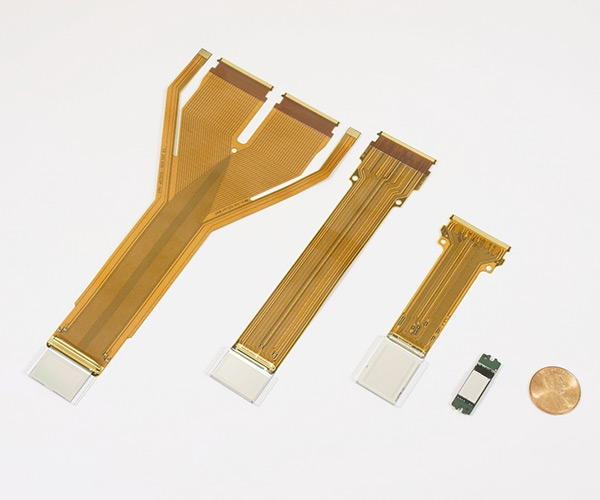

D-ILA Device
Technical Details
D-ILA is a reflective display device that combines a silicon substrate with densely arranged pixels and vertically aligned liquid-crystal technology.
This structure achieves both high brightness and high contrast.
• Compact and High-Density Structure
On the silicon substrate of the D-ILA device, mirror-like electrodes (reflective pixel electrodes) are arranged, and CMOS-based drive circuits are embedded beneath them.
This design maximizes the pixel aperture ratio up to the theoretical limit of the CMOS process.
The opposing glass substrate has transparent electrodes, and the voltage applied between the pixel and transparent electrodes controls the orientation of the liquid crystal.
Our proprietary vertically aligned liquid-crystal technology achieves one of the highest contrast ratios in the industry, while the use of an inorganic alignment layer ensures high reliability.
Since production began in 1997, we have maintained a proven mass-production record as a pioneer in the industry.
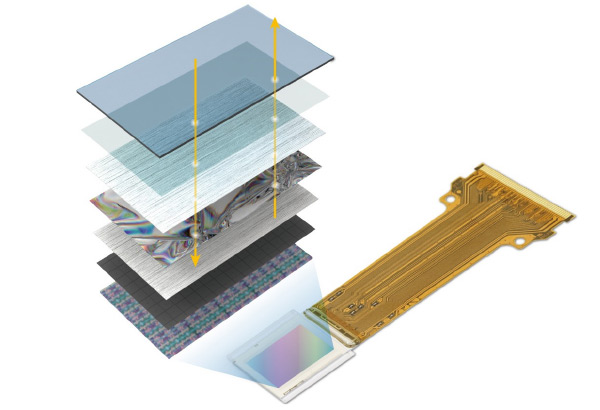
Structure of Compact and High-Density D-ILA Device
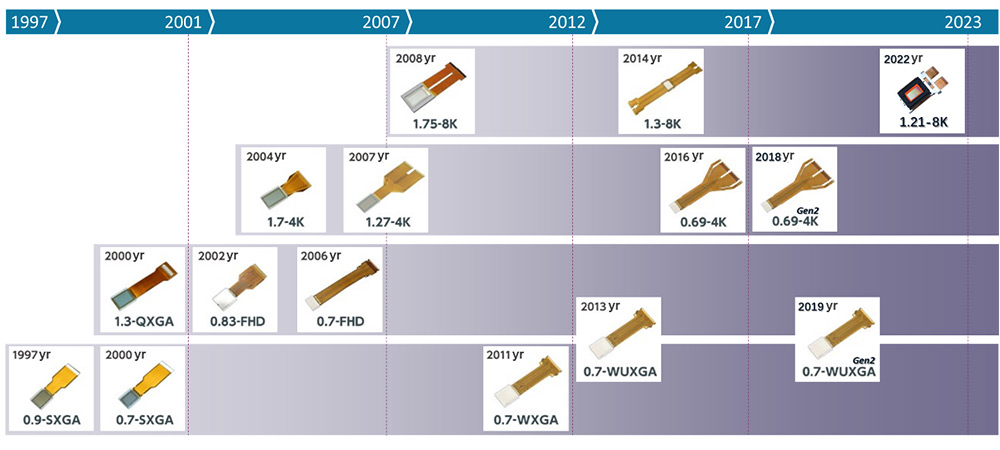
History of D-ILA Devices
• High Contrast
D-ILA employs vertically aligned liquid crystals using our proprietary inorganic alignment layer.
By optimizing pixel-surface flattening, minimizing inter-pixel gaps, and precisely controlling cell-gap thickness, the device achieves high contrast—an essential factor for high-definition imaging.
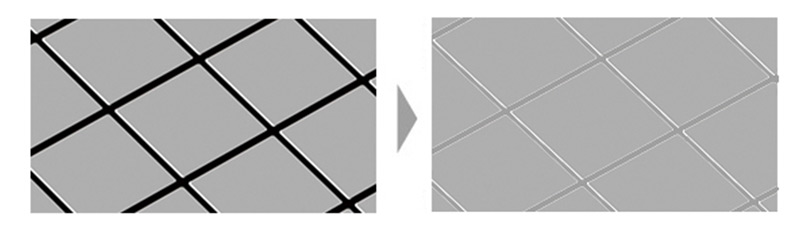
(Images are for illustrative purposes.)
Minimized Inter-Pixel Gap and Surface Flattening
• Precise Liquid-Crystal Driving
D-ILA realizes smooth gradation expression through high-precision analog driving.
It also supports unique digital driving systems such as frame-scan control, compatible with pixel-shifting and 3D applications.
These driving methods are optimized for various application characteristics, ensuring accurate and stable image performance.
Products Incorporating This Technology
Examples of products incorporating this technology


